Plumeria – Frangipani.
Family Apocynaceae > Subfamily Rauvolfioideae > Tribe Plumerieae > Subtribe Plumeriinae.
Many sources recognise 6 or 8 species but some up to 20.
There are over 100 other names regarded as either synonyms, subspecies or varieties.
Well recognised and commonly cultivated are P. obtusa, P. rubra and P. pudica.
Trees or shrubs from 2 to 8 m high mostly with a thick, rounded crown.
The branches are thick and fleshy and branchlets have rounded ends.
They break easily and exude a white latex that is a skin irritant and can be poisonous.
The bark is green to grey and there are leaf scars.
They are evergreen, deciduous or semi-deciduous.
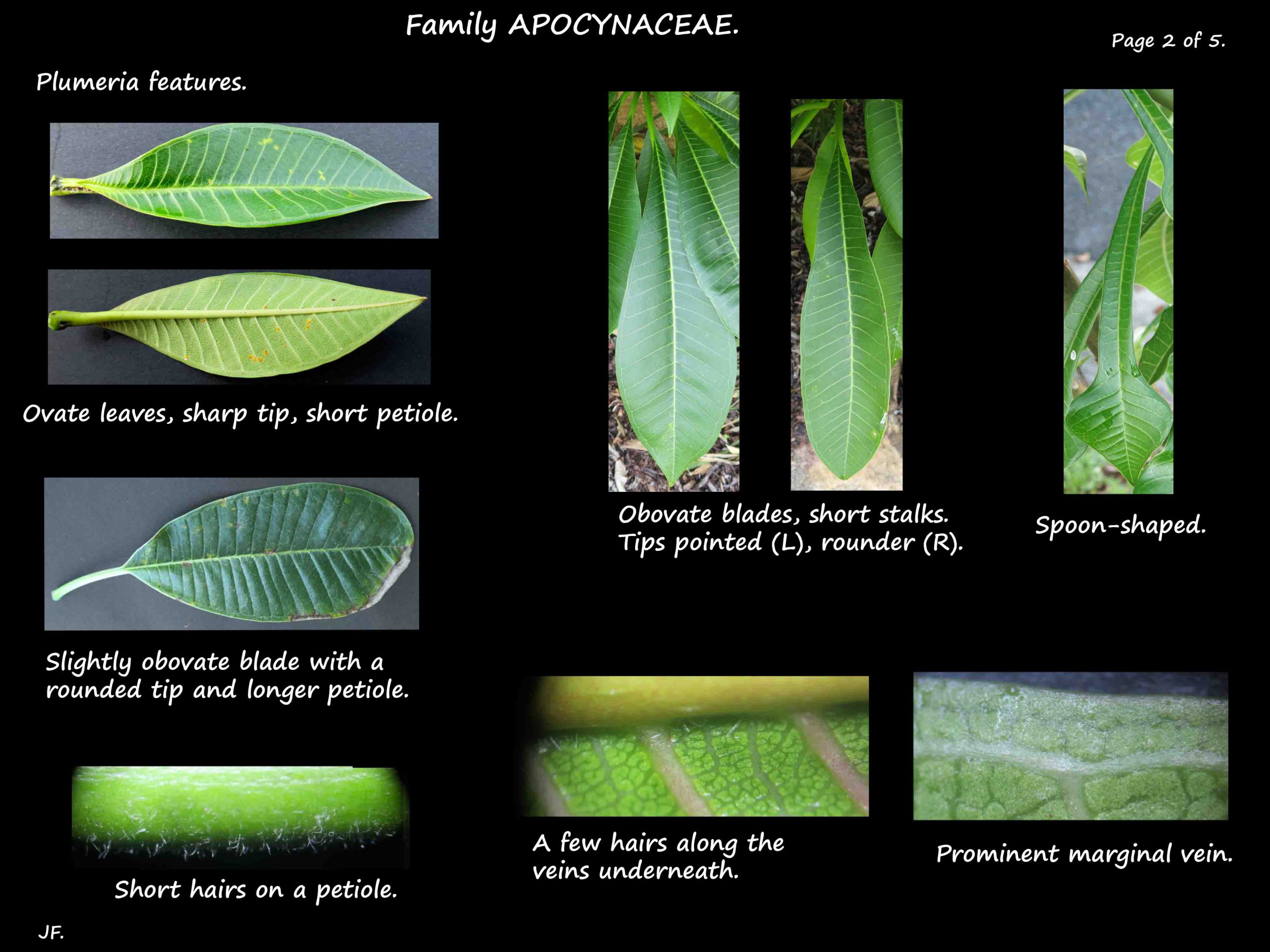
The alternate leaves are arranged in a spiral at the ends of the branches.
The simple, dark green often glossy leaves are paler underneath with a smooth edge.
The shape varies – long and narrow, ovate, obovate, lance or spoon-shaped.
The tip can be blunt, rounded or pointed.
They are 20 to 50 cm long and have prominent veins underneath.
Some have hairs on the short stalks and on new leaves.
Some varieties or cultivars are paler, variegated or have have a red edge.
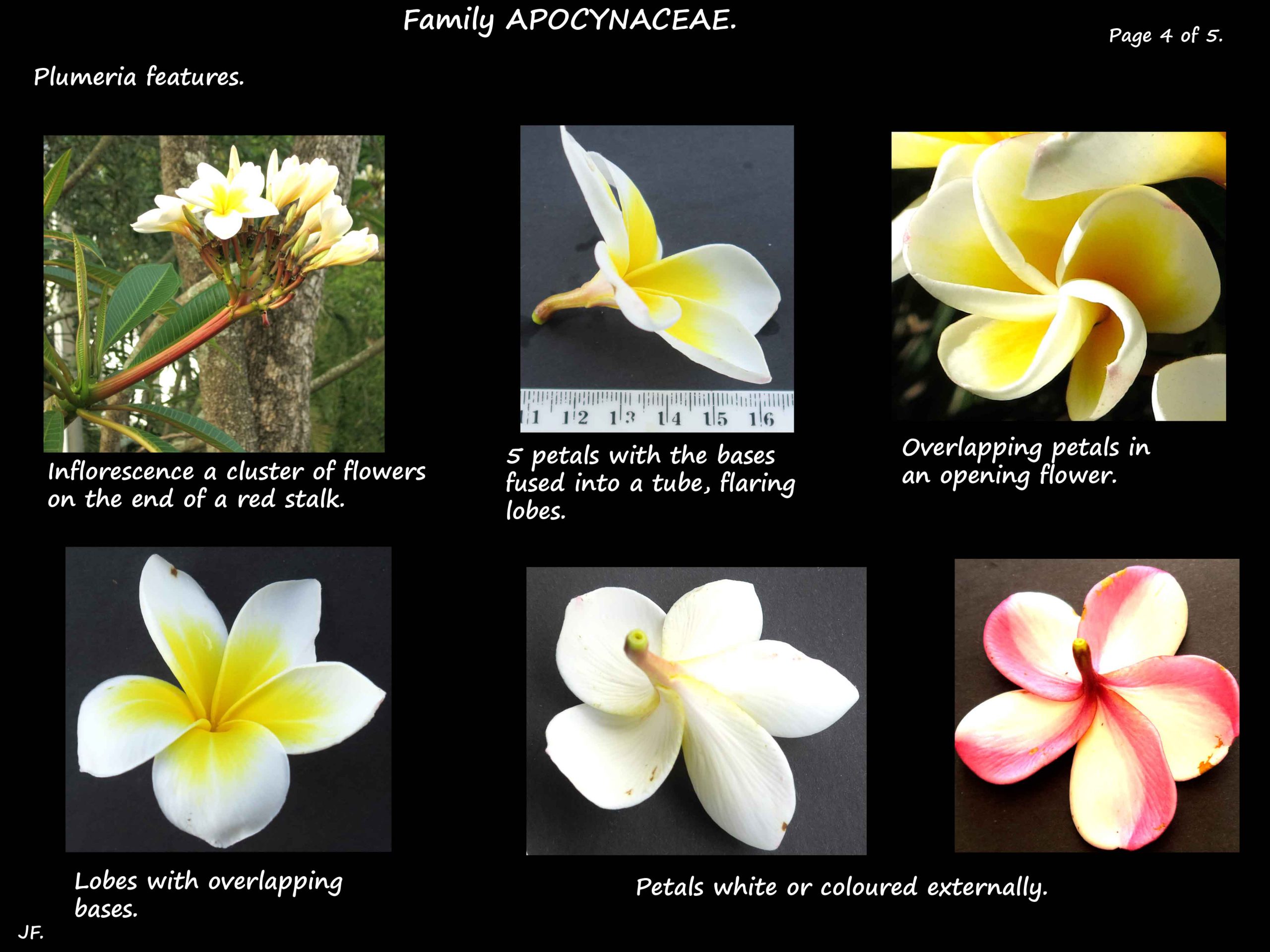
Inflorescences are terminal or axillary clusters of highly scented flowers.
The funnel-shaped flowers are 4 to 8 cm wide although some cultivars are up to 10 cm.
The bases of the 5 waxy petals are fused into a tube and the lobes flare out.
The bases of the lobes overlap and one edge may be slightly curled giving a propeller appearance.
The width of the lobes varies between species.
There are hairs inside the corolla tube.
The common white flowers with yellow centres are seen in P. obtusa, P. pudica and P. rubra varieties.
P. rubra has petals in shades of red.
The 5 stamens and the ovary are at the base of the corolla tube.
The arrowhead-shaped anthers converge above the ovary but are free.
The ovary, a few mms long, has 2 carpels with a short style and a 2-lobed stigma.
The fruit are cylindrical follicles, often paired, and up to 18 cm long.
They are rarely seen in cultivated plants where propagation is by cuttings.
There are hundreds of cultivars and hybrids mostly from P. rubra and P. obtusa.
Most plants seen are cultivars and these offer evergreen plants and some that flower all the time.
Colours include white, yellow, pink, cream and apricot most with yellow centres.
Plumeria obtusa.
There are over 30 synonyms including P. clusioides which some regard as a species.
The plant is commonly sold as ‘Singapore’, ‘Singapore White’ or ‘Singapore frangipani’.
Evergreen, obovate leaves have blunt tips and the 4 cm flowers are white with yellow centres.
Plumeria rubra.
A deciduous tree with leaves to 50 cm long and red flowers.
Hybrids may be a compact, semi-deciduous shrub with flowers in many colours.
Some regard these variations as separate species or just varieties.
Flowers may be shades of pink or red with a yellow centre.
Others are a pure bright yellow, yellow with pink tinges or white with apricot.
Plumeria pudica.
A tall, narrow, evergreen tree or shrub with long, straight largely unbranched stems.
The very base may be bare but the rest is covered in leaves, dense at the top.
The leaves, on short stalks, are arranged in a spiral.
They are spoon-shaped with a long narrow base and an expanded end with a tapering tip.
They are a glossy, mid-green with prominent veins.
Inflorescences are axillary with a cluster of flowers at the end of a long stalk.
Flowers appear throughout the year.
Flowers are white with a small yellow centre.
Hybrids come with variegated leaves or pink flowers.
J.F.